Difference between revisions of "Conversion rules"
m (naming convention) |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Compiler]] | [[Category:Compiler]] | ||
[[Category:ECMA]] | [[Category:ECMA]] | ||
| − | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 12: | ||
* 8.15.3 Validity: ''Conversion principle'': No type may both conform and convert to another. | * 8.15.3 Validity: ''Conversion principle'': No type may both conform and convert to another. | ||
| + | This has to be verified for all static types. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: At runtime for dynamic types this principle cannot be easily guaranteed. See [[#Appendix|appendix]] for more information. | ||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
As the conversion rules are strongly dual, each example can be transformed to show the issue for its sibling. | As the conversion rules are strongly dual, each example can be transformed to show the issue for its sibling. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 23: | ||
<code>[eiffel,N] | <code>[eiffel,N] | ||
| − | class A[G] | + | class |
| + | A [G] | ||
| + | |||
convert | convert | ||
| − | + | as_a: {A [G]} | |
| + | |||
feature | feature | ||
| − | + | as_a: A [G] | |
do end | do end | ||
| + | |||
end | end | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
| − | The conversion to '''A[G]''' should indeed not be valid because they are conform. | + | The conversion to '''A [G]''' should indeed not be valid because they are conform. |
The only rule that matters in our case is '''VYCQ(3)'''. | The only rule that matters in our case is '''VYCQ(3)'''. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 41: | ||
What VYCQ(3) asks is the following | What VYCQ(3) asks is the following | ||
| − | Is A[ANY] conform to A[G]? | + | Is <e>A [ANY]</e> conform to <e>A [G]</e>? |
The answer is '''no''' and thus the code regarded as valid. | The answer is '''no''' and thus the code regarded as valid. | ||
| Line 52: | Line 58: | ||
<code>[eiffel,N] | <code>[eiffel,N] | ||
| − | class A[G] | + | class |
| + | A [G] | ||
| + | |||
convert | convert | ||
| − | + | as_a: {A [STRING]} | |
| + | |||
feature | feature | ||
| − | + | as_a: A [STRING] | |
do end | do end | ||
| + | |||
end | end | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
| Line 64: | Line 74: | ||
The interesting rule is again '''VYCQ(3)''': | The interesting rule is again '''VYCQ(3)''': | ||
| − | Is A[ANY] conform to A[STRING]? | + | Is <e>A [ANY]</e> conform to <e>A [STRING]</e>? |
The answer is '''no''' and thus the code regarded as valid. | The answer is '''no''' and thus the code regarded as valid. | ||
| + | |||
Summary: | Summary: | ||
* correct result: <font color="green">invalid</font> | * correct result: <font color="green">invalid</font> | ||
| Line 78: | Line 89: | ||
<code>[eiffel,N] | <code>[eiffel,N] | ||
| − | class A[G,H] | + | class |
| + | A [G,H] | ||
| + | |||
convert | convert | ||
| − | + | as_a: {A [G,G]} | |
| + | |||
feature | feature | ||
| − | + | as_a: A [G,G] | |
do end | do end | ||
| + | |||
end | end | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
| Line 89: | Line 104: | ||
'''VYCQ(3)''': | '''VYCQ(3)''': | ||
| − | Is A[ANY,ANY] conform to A[G,G]? | + | Is <e>A [ANY,ANY]</e> conform to <e>A [G,G]</e>? |
The answer is '''no''' and thus the code regarded as valid. | The answer is '''no''' and thus the code regarded as valid. | ||
| + | |||
Summary: | Summary: | ||
* correct result: <font color="green">invalid</font> | * correct result: <font color="green">invalid</font> | ||
| Line 98: | Line 114: | ||
* complex rule: <font color="green">invalid</font> | * complex rule: <font color="green">invalid</font> | ||
====Example 4==== | ====Example 4==== | ||
| − | This is an example which is valid under the current rules and should remain valid. Even though we inherit from A[ANY] the conversion to A[STRING] should be valid. | + | This is an example which is valid under the current rules and should remain valid. Even though we inherit from A [ANY] the conversion to A[STRING] should be valid. |
* eweasel test: convert-to-base-class-inherited | * eweasel test: convert-to-base-class-inherited | ||
<code>[eiffel,N] | <code>[eiffel,N] | ||
| − | class A[G] | + | class A [G] |
end | end | ||
| − | class B[G] | + | class |
| + | B [G] | ||
| + | |||
inherit | inherit | ||
| − | + | A [ANY] | |
| + | |||
convert | convert | ||
| − | + | as_b: {A [STRING]} | |
| + | |||
feature | feature | ||
| − | + | as_b: A [STRING] | |
do end | do end | ||
| + | |||
end | end | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
| Line 119: | Line 140: | ||
'''VYCQ(3)''': | '''VYCQ(3)''': | ||
| − | Is B[ANY] conform to A[STRING]? | + | Is <e>B [ANY]</e> conform to <e>A [STRING]</e>? |
The answer is '''no''' and thus the code regarded as valid. | The answer is '''no''' and thus the code regarded as valid. | ||
| Line 132: | Line 153: | ||
This is the second example which is valid under the current rules. The code is valid as the ''Conversion principle'' cannot possibly be violated. | This is the second example which is valid under the current rules. The code is valid as the ''Conversion principle'' cannot possibly be violated. | ||
| − | * eweasel test: convert-to-base-class- | + | * eweasel test: convert-to-base-class-inherited2 |
<eiffel> | <eiffel> | ||
| − | class A[G,H] | + | class A [G,H] |
end | end | ||
| − | class B[G->INTEGER,H->DOUBLE] | + | class |
| + | B [G -> INTEGER,H -> DOUBLE] | ||
inherit | inherit | ||
| − | + | A [G,H] | |
| + | |||
convert | convert | ||
| − | + | as_a: {A [DOUBLE,INTEGER]} | |
| + | |||
feature | feature | ||
| − | + | as_a: A [DOUBLE,INTEGER] | |
do end | do end | ||
| + | |||
end | end | ||
</eiffel> | </eiffel> | ||
'''VYCQ(3)''': | '''VYCQ(3)''': | ||
| − | Is B[INTEGER,DOUBLE] conform to A[DOUBLE,INTEGER]? | + | Is <e>B [INTEGER,DOUBLE]</e> conform to <e> A[DOUBLE,INTEGER]</e>? |
The answer is '''no''' and thus the code regarded as valid. | The answer is '''no''' and thus the code regarded as valid. | ||
| Line 161: | Line 186: | ||
====Example 6==== | ====Example 6==== | ||
| − | |||
| − | * eweasel test: convert-to-base-class- | + | * eweasel test: convert-to-base-class-inherited3 |
<eiffel> | <eiffel> | ||
| − | class A[G] | + | class A [G] |
end | end | ||
| − | class B[G->INTEGER_REF] | + | class |
| + | B [G -> INTEGER_REF] | ||
| + | |||
inherit | inherit | ||
| − | + | A [G] | |
| + | |||
convert | convert | ||
| − | + | as_a: {A [DOUBLE]} | |
| + | |||
feature | feature | ||
| − | + | as_a: A [DOUBLE] | |
do end | do end | ||
| + | |||
end | end | ||
</eiffel> | </eiffel> | ||
'''VYCQ(3)''': | '''VYCQ(3)''': | ||
| − | Is B[INTEGER_REF] conform to A[DOUBLE]? | + | Is <e>B [INTEGER_REF]</e> conform to <e>A [DOUBLE]</e>? |
The answer is '''no''' and thus the code regarded as valid. | The answer is '''no''' and thus the code regarded as valid. | ||
| Line 193: | Line 222: | ||
==Understanding the matter== | ==Understanding the matter== | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Type-conversion-illustration.png|thumb|Type Diagram]] | |
| − | + | If we take the inheritance hierarchy of an Eiffel system it can be abstracted to a directed acyclic graph. A an valid type (TARGET) for conversion has the following properties: | |
| + | * The constraint does not conform to it (VYC*(3)). | ||
| + | * There exists no valid generic derivation of CT which is conform to the TARGET. | ||
| − | == | + | All these properties include the normal cases (for example CT contains no formals). |
| + | |||
| + | The illustration on the right shows where conversion is valid and might help to visualize the matter a little bit. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Wildcard rule== | ||
Instead of restricting VYCQ(2) and VYCP(2) to non-generic types we allow generic types too. As VYC*(2) is even using the notion of ''current type'', it might indeed be possible that it was the authors original intention. | Instead of restricting VYCQ(2) and VYCP(2) to non-generic types we allow generic types too. As VYC*(2) is even using the notion of ''current type'', it might indeed be possible that it was the authors original intention. | ||
We define an additional function ''FTN'' which replaces every formal generic with another type: | We define an additional function ''FTN'' which replaces every formal generic with another type: | ||
| − | * By a wildcard type, which is conform to anything if the formals constraint type is not frozen. | + | * By a wildcard type (*), which is conform to anything if the formals constraint type is not frozen. |
* By the (single) frozen type which occurs in the constraint of the formal. | * By the (single) frozen type which occurs in the constraint of the formal. | ||
The wildcard type virtually makes the conformance check for this formal obsolete, as the result is always true. | The wildcard type virtually makes the conformance check for this formal obsolete, as the result is always true. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
The new version could look like this: | The new version could look like this: | ||
| Line 212: | Line 246: | ||
* VYCQ'(2) ''FTN(CT)'' does not conform to ''TARGET'' | * VYCQ'(2) ''FTN(CT)'' does not conform to ''TARGET'' | ||
| − | + | ====Wildcard rule applied to some examples==== | |
| + | '''Example 4 for VYCQ'(2):''' | ||
| − | + | Is <e>B [*]</e> conform to <e>A [STRING]</e>? | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The answer is '''no''' and therefore the code '''valid'''.<br> | |
| + | This is because ''B'' only inherits from ''A [ANY]''. | ||
| − | |||
| + | '''Example 5 for VYCQ'(2):''' | ||
| − | + | Is <e>B [INTEGER,DOUBLE]</e> conform to <e>A [DOUBLE,INTEGER]</e>? | |
| − | + | The answer is '''no''' and therefore the code '''valid'''. | |
| − | + | '''Example 6 for VYCQ'(2):''' | |
| + | Is <e>B [*]</e> conform to <e>A [DOUBLE]</e>? | ||
| − | ''' | + | The answer is '''yes''' and therefore the code '''invalid'''. But it should be '''valid''' because the constraint INTEGER_REF and the fact that DOUBLE is frozen make it impossible to create a type which satisfies both, the conformance to INTEGER_REF and to DOUBLE. |
| − | + | One could avoid this shortcoming by a more complex definition of the wildcard type: | |
| + | The wildcard type matches only frozen types which fulfill the constraint. | ||
| − | The | + | It would give more accuracy at the expense of a more complicated rule. The idea of taking the TARGET and see whether one can build a generic derivation of CT which conforms to the constraint, what our patch to the wildcard rule basically does, can be formulated as another rule: |
| + | ==Pattern matching rule== | ||
| + | |||
| + | In case we check a class, which has at least one formal generic type parameter we want to find out, whether it is possible to derive a type which is conform to the constraint and to the type where we convert to. If such a type exists, the conversion is invalid as it violates the ''Conversion Principle''. | ||
| − | + | The algorithm is explained together with Example 6: | |
| − | + | For every conversion we check whether the base class of the class we check is conform to the base class of the type we convert to. | |
| + | * If CT inherits from the base class of TARGET, we call that derivation of the same base class CPCT (for corresponding parent of CT). | ||
| + | In Example 6: | ||
| + | <e>B</e> inherits from <e>A</e>. | ||
| + | TARGET: <e>A [DOUBLE]</e> | ||
| + | CPCT: <e>A [G]</e> | ||
| − | + | If that is true, the generic derivation might contain formal generic parameters. We perform a pattern matching and replace the formals with the according derivation found in the type we convert to. | |
| + | * Find for every formal at position ''i'' of CPCT the corresponding class type found at position i in TARGET. Create a new instance called TTC (Type to check) of CT by using the class types for all formals used. | ||
| + | Formal G in CPCT has position 1. | ||
| + | The type at position 1 in TARGET is <e>DOUBLE</e>. | ||
| + | We replace the formal G in CT with <e>DOUBLE</e> and obtain TTC: <e>B [DOUBLE]</e> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We take this type and check whether it satisfies the constraint and is conform to the type we convert to. If both hold at the same time there exists a valid derivation of CT and therefore the ''Conversion Principle'' violated. | ||
| + | * Check whether TTC is a valid generic derivation of CT and whether it conforms to TARGET | ||
| − | ''' | + | <e>B [DOUBLE]</e> does '''not''' satisfy the constraint (<e>INTEGER_REF</e>). |
| + | <e>B [DOUBLE]</e> is conform to TARGET (<e>A [DOUBLE]</e>). | ||
| − | + | As not both statements hold it is a valid conversion. | |
| − | + | It can be quite tricky to check this rule as for example: | |
| + | <eiffel> | ||
| + | class | ||
| + | B [G -> H, H -> G] | ||
| − | + | inherit | |
| + | A [G] | ||
| − | + | convert | |
| + | as_a: {A [STRING]} | ||
| − | The | + | feature |
| + | as_a: A [STRING] | ||
| + | do end | ||
| + | |||
| + | end | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
| + | We would obtain a TTC which looks like this: B[STRING,G]<br> | ||
| + | Now one would have to define, whether this type satisfies the constraint or not. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Check at a different level== | ||
| + | As it turns out to be quite tricky to check validity on the class declaration level one could try to do it a bit later. The following three possibilities have different advantages and disadvantages: | ||
| + | ====Level 1: Class declaration==== | ||
| + | It is the most complex part to check but one would do the check only once. | ||
| + | ====Level 2: Type declaration==== | ||
| + | This solution is much easier to check and to explain to a user (as there is now a particular failing instance). With this solution the difficult part, which is to check that there is no valid generic derivation of CT which is conform to the TARGET, is avoided. The check is done at every generic type derivation where there are any conversion rules for the corresponding base class. So there are possibly more checks necessary compared to a level 1 check. | ||
| + | * Note: One can create new Types dynamically at runtime by using the <e>INTERNAL</e> class. However this does not introduce any new conversions as the code itself remains static. Therefore it seems ok not to check them. | ||
| + | ===='''Level 3: Attachment'''==== | ||
| + | The check is done for every attachment (<e>a := b</e>). This seems to be even more expensive than a level 2 check as one has to check for each attachment both: conformance and conversion. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Drop the Conversion Principle== | ||
| + | As a radical alternative one could also be totally open and say the following is valid code: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <eiffel> | ||
| + | class | ||
| + | A [G] | ||
| + | |||
| + | convert | ||
| + | as_a: {A [STRING]} | ||
| + | |||
| + | end | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
| + | As soon as we find out statically that we have type conformance in a particular case, we do not do a conversion. So one would only do a conversion if it is necessary. | ||
| + | Actually this rule would drop the conversion principle at all. | ||
| + | This seems to be ok as the conversion principle (without additional rules) can be violated at runtime. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Appendix== | ||
| + | ====Conversion principle at runtime==== | ||
| + | Through the class <e>INTERNAL</e> one is able to create new types at runtime. With this ability it is possible to violate the ''Conversion Principle'' at runtime. | ||
| + | It can also be violated without creating dynamically new types as the following code shows: | ||
| + | <eiffel> | ||
| + | class X | ||
| + | convert | ||
| + | as_y: {Y} | ||
| + | feature | ||
| + | as_y: Y | ||
| + | do end | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | class Y | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | |||
| + | class XY | ||
| + | inherit | ||
| + | X | ||
| + | Y | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | class | ||
| + | TEST | ||
| + | |||
| + | feature | ||
| + | test | ||
| + | local | ||
| + | x: X | ||
| + | xy: XY | ||
| + | do | ||
| + | create xy | ||
| + | x := xy | ||
| + | -- A conversion is done. The dynamic types conform. | ||
| + | needs_y (x) | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | |||
| + | needs_y (y: Y) | ||
| + | do end | ||
| + | |||
| + | end | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
Latest revision as of 02:27, 20 May 2013
Contents
Introduction
This article discusses issues recently discovered for the following two validity rules:
- 8.15.7 Validity: Conversion Procedure rule, Validity code: VYCP
- 8.15.8 Validity: Conversion Query rule, Validity code: VYCQ
There are cases where both of them violate the conversion principle:
- 8.15.3 Validity: Conversion principle: No type may both conform and convert to another.
This has to be verified for all static types.
Note: At runtime for dynamic types this principle cannot be easily guaranteed. See appendix for more information.
Examples
As the conversion rules are strongly dual, each example can be transformed to show the issue for its sibling.
Example 1
We have a conversion to the current type of the class. It should not be allowed. Currently no rule rejects this code.
- eweasel test: convert-to-current-type
class A [G] convert as_a: {A [G]} feature as_a: A [G] do end end
The conversion to A [G] should indeed not be valid because they are conform.
The only rule that matters in our case is VYCQ(3).
What VYCQ(3) asks is the following
IsA [ANY]conform toA [G]?
The answer is no and thus the code regarded as valid.
Summary:
- correct result: invalid
- old rules: valid
- wildcard rule: invalid
- complex rule: invalid
Example 2
This example shows a special case which is valid under the current rule but can possibly lead to a conflict between conformance and conversion.
- eweasel test: convert-to-possible-actual-type
class A [G] convert as_a: {A [STRING]} feature as_a: A [STRING] do end end
In the case where G's actual type parameter is a subtype of STRING it yields in a situation where the two types are conform again.
The interesting rule is again VYCQ(3):
IsA [ANY]conform toA [STRING]?
The answer is no and thus the code regarded as valid.
Summary:
- correct result: invalid
- old rules: valid
- wildcard rule: invalid
- complex rule: invalid
Example 3
- eweasel test: convert-to-base-class
class A [G,H] convert as_a: {A [G,G]} feature as_a: A [G,G] do end end
VYCQ(3):
IsA [ANY,ANY]conform toA [G,G]?
The answer is no and thus the code regarded as valid.
Summary:
- correct result: invalid
- old rules: valid
- wildcard rule: invalid
- complex rule: invalid
Example 4
This is an example which is valid under the current rules and should remain valid. Even though we inherit from A [ANY] the conversion to A[STRING] should be valid.
- eweasel test: convert-to-base-class-inherited
class A [G] end class B [G] inherit A [ANY] convert as_b: {A [STRING]} feature as_b: A [STRING] do end end
VYCQ(3):
IsB [ANY]conform toA [STRING]?
The answer is no and thus the code regarded as valid.
Summary:
- correct result: valid
- old rules: valid
- wildcard rule: valid
- complex rule: valid
Example 5
This is the second example which is valid under the current rules. The code is valid as the Conversion principle cannot possibly be violated.
- eweasel test: convert-to-base-class-inherited2
class A [G,H] end class B [G -> INTEGER,H -> DOUBLE] inherit A [G,H] convert as_a: {A [DOUBLE,INTEGER]} feature as_a: A [DOUBLE,INTEGER] do end end
VYCQ(3):
IsB [INTEGER,DOUBLE]conform toA[DOUBLE,INTEGER]?
The answer is no and thus the code regarded as valid.
Summary:
- correct result: valid
- old rules: valid
- wildcard rule: valid
- complex rule: valid
Example 6
- eweasel test: convert-to-base-class-inherited3
class A [G] end class B [G -> INTEGER_REF] inherit A [G] convert as_a: {A [DOUBLE]} feature as_a: A [DOUBLE] do end end
VYCQ(3):
IsB [INTEGER_REF]conform toA [DOUBLE]?
The answer is no and thus the code regarded as valid.
Summary:
- correct result: valid
- old rules: valid
- wildcard rule: invalid
- complex rule: valid
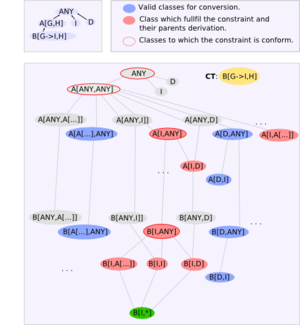
Understanding the matter
If we take the inheritance hierarchy of an Eiffel system it can be abstracted to a directed acyclic graph. A an valid type (TARGET) for conversion has the following properties:
- The constraint does not conform to it (VYC*(3)).
- There exists no valid generic derivation of CT which is conform to the TARGET.
All these properties include the normal cases (for example CT contains no formals).
The illustration on the right shows where conversion is valid and might help to visualize the matter a little bit.
Wildcard rule
Instead of restricting VYCQ(2) and VYCP(2) to non-generic types we allow generic types too. As VYC*(2) is even using the notion of current type, it might indeed be possible that it was the authors original intention.
We define an additional function FTN which replaces every formal generic with another type:
- By a wildcard type (*), which is conform to anything if the formals constraint type is not frozen.
- By the (single) frozen type which occurs in the constraint of the formal.
The wildcard type virtually makes the conformance check for this formal obsolete, as the result is always true.
The new version could look like this:
- VYCP'(2) FTN(SOURCE) does not conform to CT
- VYCQ'(2) FTN(CT) does not conform to TARGET
Wildcard rule applied to some examples
Example 4 for VYCQ'(2):
IsB [*]conform toA [STRING]?
The answer is no and therefore the code valid.
This is because B only inherits from A [ANY].
Example 5 for VYCQ'(2):
IsB [INTEGER,DOUBLE]conform toA [DOUBLE,INTEGER]?
The answer is no and therefore the code valid.
Example 6 for VYCQ'(2):
IsB [*]conform toA [DOUBLE]?
The answer is yes and therefore the code invalid. But it should be valid because the constraint INTEGER_REF and the fact that DOUBLE is frozen make it impossible to create a type which satisfies both, the conformance to INTEGER_REF and to DOUBLE.
One could avoid this shortcoming by a more complex definition of the wildcard type:
The wildcard type matches only frozen types which fulfill the constraint.
It would give more accuracy at the expense of a more complicated rule. The idea of taking the TARGET and see whether one can build a generic derivation of CT which conforms to the constraint, what our patch to the wildcard rule basically does, can be formulated as another rule:
Pattern matching rule
In case we check a class, which has at least one formal generic type parameter we want to find out, whether it is possible to derive a type which is conform to the constraint and to the type where we convert to. If such a type exists, the conversion is invalid as it violates the Conversion Principle.
The algorithm is explained together with Example 6:
For every conversion we check whether the base class of the class we check is conform to the base class of the type we convert to.
- If CT inherits from the base class of TARGET, we call that derivation of the same base class CPCT (for corresponding parent of CT).
In Example 6:Binherits fromA. TARGET:A [DOUBLE]CPCT:A [G]
If that is true, the generic derivation might contain formal generic parameters. We perform a pattern matching and replace the formals with the according derivation found in the type we convert to.
- Find for every formal at position i of CPCT the corresponding class type found at position i in TARGET. Create a new instance called TTC (Type to check) of CT by using the class types for all formals used.
Formal G in CPCT has position 1. The type at position 1 in TARGET isDOUBLE. We replace the formal G in CT withDOUBLEand obtain TTC:B [DOUBLE]
We take this type and check whether it satisfies the constraint and is conform to the type we convert to. If both hold at the same time there exists a valid derivation of CT and therefore the Conversion Principle violated.
- Check whether TTC is a valid generic derivation of CT and whether it conforms to TARGET
B [DOUBLE]does not satisfy the constraint (INTEGER_REF).B [DOUBLE]is conform to TARGET (A [DOUBLE]).
As not both statements hold it is a valid conversion.
It can be quite tricky to check this rule as for example:
class B [G -> H, H -> G] inherit A [G] convert as_a: {A [STRING]} feature as_a: A [STRING] do end end
We would obtain a TTC which looks like this: B[STRING,G]
Now one would have to define, whether this type satisfies the constraint or not.
Check at a different level
As it turns out to be quite tricky to check validity on the class declaration level one could try to do it a bit later. The following three possibilities have different advantages and disadvantages:
Level 1: Class declaration
It is the most complex part to check but one would do the check only once.
Level 2: Type declaration
This solution is much easier to check and to explain to a user (as there is now a particular failing instance). With this solution the difficult part, which is to check that there is no valid generic derivation of CT which is conform to the TARGET, is avoided. The check is done at every generic type derivation where there are any conversion rules for the corresponding base class. So there are possibly more checks necessary compared to a level 1 check.
- Note: One can create new Types dynamically at runtime by using the
INTERNALclass. However this does not introduce any new conversions as the code itself remains static. Therefore it seems ok not to check them.
Level 3: Attachment
The check is done for every attachment (a := b). This seems to be even more expensive than a level 2 check as one has to check for each attachment both: conformance and conversion.
Drop the Conversion Principle
As a radical alternative one could also be totally open and say the following is valid code:
class A [G] convert as_a: {A [STRING]} end
As soon as we find out statically that we have type conformance in a particular case, we do not do a conversion. So one would only do a conversion if it is necessary. Actually this rule would drop the conversion principle at all. This seems to be ok as the conversion principle (without additional rules) can be violated at runtime.
Appendix
Conversion principle at runtime
Through the class INTERNAL one is able to create new types at runtime. With this ability it is possible to violate the Conversion Principle at runtime.
It can also be violated without creating dynamically new types as the following code shows:
class X convert as_y: {Y} feature as_y: Y do end end class Y end class XY inherit X Y end class TEST feature test local x: X xy: XY do create xy x := xy -- A conversion is done. The dynamic types conform. needs_y (x) end needs_y (y: Y) do end end