Difference between revisions of "Replication"
(→Version) |
m (→Replication and precursor) |
||
| (157 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category:ECMA]] | ||
Author: Matthias Konrad | Author: Matthias Konrad | ||
| − | + | Related articles: | |
| − | + | * A discussion on unfolded forms in the ECMA standard: [[ECMA_unfolded]]. | |
| − | + | * A mathematical model for Eiffels dynamic binding: [[DynBindModel]]. | |
| + | * An example instantiation of the the dynamic binding model: [[DynBindModelExamples]]. | ||
| + | ====Prologue==== | ||
One definition of replication is: the action or process of reproducing or duplicating. | One definition of replication is: the action or process of reproducing or duplicating. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 16: | ||
If an unfolded form cannot be found, this has a huge impact on the standards text. The semantics of unqualified calls in the context of replicated features would for example not be defined. | If an unfolded form cannot be found, this has a huge impact on the standards text. The semantics of unqualified calls in the context of replicated features would for example not be defined. | ||
| − | ==Talking about features== | + | ====Talking about features==== |
| − | + | Before digging into the replication rules we need a clear understanding of a feature. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | There is a one to one connection between feature and Feature_body. Every feature has | + | There is a one to one connection between feature and Feature_body. Every feature has exactly one body. Every body belongs to exactly one feature. Meaning that, two different bodies belong to two different features and two different features have two different bodies. |
Have a look at this example: | Have a look at this example: | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
{|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | {|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | ||
|-valign="top" -halign="center" | |-valign="top" -halign="center" | ||
| − | |< | + | |<eiffel> |
class | class | ||
B | B | ||
| Line 29: | Line 31: | ||
f do ... end | f do ... end | ||
end | end | ||
| − | </ | + | </eiffel> |
| | | | ||
| − | < | + | <eiffel> |
class | class | ||
D | D | ||
| Line 42: | Line 44: | ||
f2 do ... end | f2 do ... end | ||
end | end | ||
| − | </ | + | </eiffel> |
|} | |} | ||
| − | The above system has two features. | + | The following sentences apply to the above system: |
| − | + | * The system has two features. | |
| + | * The feature named ''f1'' in class ''D'' and the feature named ''f'' in class ''B'' are one and the same feature. | ||
| + | * Feature ''f1'' of class ''D'' and feature ''f'' of class ''B'' are the same feature. | ||
| + | * Feature ''f2'' of class ''D'' or the feature named ''f2'' in class ''D''. This feature has its body defined in class ''D''. | ||
By saying feature, we indirectly reference a certain Feature_body. Indirectly, because we can say: "feature ''f'' of a class ''D''", when the Feature_body of ''f'' belongs to an Ancestor class ''A'' of ''D'' (Given that ''f'' is not redeclared on the inheritance path between ''A'' and ''D''). | By saying feature, we indirectly reference a certain Feature_body. Indirectly, because we can say: "feature ''f'' of a class ''D''", when the Feature_body of ''f'' belongs to an Ancestor class ''A'' of ''D'' (Given that ''f'' is not redeclared on the inheritance path between ''A'' and ''D''). | ||
| − | The name of feature ''f'' is always the name stated in its Feature_body. A feature may have different names in different classes (through renaming). It is thus legal to say: "Feature ''f'' with name ''fn'' in class ''D'', when feature ''f'' is renamed to ''fn'' somewhere along the according inheritance path. | + | The name of feature ''f'' is always the name stated in its Feature_body. A feature may have different names in different classes (through renaming). It is thus legal to say: "Feature ''f'' with name ''fn'' in class ''D''", when feature ''f'' is renamed to ''fn'' somewhere along the according inheritance path. |
| − | + | When we talk about feature bodies we are not strictly bound to the bodies occurring in the programs text. We may also denote the bodies that are results of folded forms. Examples are the body of a synonym or the body of a call-equivalent of an inline-agent or the body of a replicate as we will later see. | |
| − | ==Version== | + | ====Version==== |
| + | A '''version''' of a feature ''f'' is a feature ''f2'' different from ''f'' that is a redeclaration from either ''f'' or a '''version''' of ''f''. | ||
| + | ====Talking about replicates==== | ||
| + | The term feature is now clear. A replicated features seems to be just an other feature. But where is its body? In the above Eiffel system there is certainly some replication going on. But there are no bodies for those replicated features. | ||
| − | + | This informal reasoning suggests that a replicated feature should be defined by an unfolded form. Given that this is defined, there is finally something like a replicated feature. Every replicated feature has a feature from which it is replicated from. It could be said, feature ''r'' is a replicate of feature ''f'' or feature ''r'' is replicated from feature ''f''. | |
| − | + | There is an other problem, it needs to be defined, when there is a need for a replicated feature of a certain feature. Altogether there are two things left to be defined. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | ====When is a replicated feature needed==== |
| + | If a class has two feature names that refer to the same feature, both features need to be replicated. If a class has two features ''f1'' and ''f2'' where ''f2'' is a version of ''f1'' then feature ''f1'' needs to be replicated. | ||
| − | + | For the above Eiffel system with classes ''B'' and ''D'' there is a need for replication. The feature with name ''f2'' in class ''D'' is a version of the feature with name ''f1'' in ''D''. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ====The replicated feature==== | |
| + | The replicated feature ''r'' of a feature ''f'' is a redeclaration of ''f''. The body of ''r'' is almost a copy of feature ''f''. Some features need to be renamed. In principal it is a transposition of feature ''f'' to the class in which the replication is needed. How exactly the transposition is done needs some thought. Here some examples should give a general understanding. | ||
| − | + | In the following system: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
{|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | {|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | ||
|-valign="top" -halign="center" | |-valign="top" -halign="center" | ||
| − | |< | + | |<eiffel> |
class | class | ||
B | B | ||
feature | feature | ||
| − | f do ... end | + | f do g end |
| + | g do ... end | ||
| + | |||
end | end | ||
| − | </ | + | </eiffel> |
| | | | ||
| − | < | + | <eiffel> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
class | class | ||
D | D | ||
inherit | inherit | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
B | B | ||
| − | rename f as | + | rename f as f1, g as g1 select f1, g1 end |
| − | + | B | |
| − | f2 | + | rename f as f2, g as g2 end |
end | end | ||
| − | </ | + | </eiffel> |
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Both feature ''f'' and ''g'' of class ''B'' need to be replicated twice in class ''D''. The unfolded form of ''D'' (here called ''DU'') becomes: | |
| − | |||
{|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | {|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | ||
|-valign="top" -halign="center" | |-valign="top" -halign="center" | ||
| − | |< | + | |<eiffel> |
class | class | ||
| − | + | DU | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
inherit | inherit | ||
B | B | ||
| − | rename f as f1, | + | rename f as f1, g as g1 redefine f1, g1 select f1, g1 end |
B | B | ||
| − | rename f as f2, g as g2 | + | rename f as f2, g as g2 redefine f2, g2 end |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
feature | feature | ||
| − | f1 do ... end | + | f1 do g1 end |
| + | g1 do ... end | ||
| + | f2 do g2 end | ||
| + | g2 do ... end | ||
end | end | ||
| − | </ | + | </eiffel> |
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | It is somewhat lame not to give a precise definition of how exactly transposition works. But it is used in other places of the Eiffel standard as well and is thus off topic to describe it here. | |
| − | + | ====Replication and inline agents==== | |
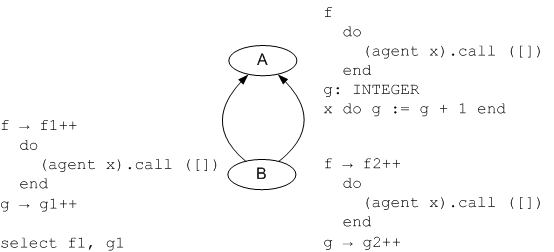
| + | It is important to analyze how this new unfolded form works together with other unfolded forms. The following system contains both an inline-agent and some features that need to be replicated: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | ||
| + | |-valign="top" -halign="center" | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | [[Image:ReplicationInlineAgent.png]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | The unfolded form of feature | + | The unfolded form of the inline agent is a normal feature in class A. The replicated features become a redeclaration of features f and g. The following picture shows the same system with everything unfolded: |
| − | + | ||
| − | The | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
{|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | {|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | ||
|-valign="top" -halign="center" | |-valign="top" -halign="center" | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | + | [[Image:ReplicationInlineAgentUnfolded.png]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | According to the current Eiffel standard this system is not valid anymore. Shared feature ''x'' is not allowed to refer to the replicated features ''g1'' and ''g2''. Feature ''x'' not being replicated comes from the fact, that class ''B'' inherits from the completely unfolded class ''A''. Otherwise the unfolding would become ambiguous. | |
| + | The unfolded system is most probably not what the programmer had in mind when he constructed it. He certainly expected feature ''x'' of the inline agent to be replicated too. | ||
| + | At the moment though, there is no such link between the inline-agent and its enclosing feature (feature ''f'') | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Replication and precursor==== | ||
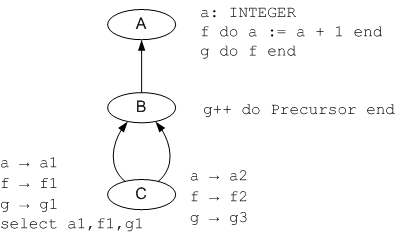
| + | The problem discussed here is similar to the previous one. It shows how the unfolded form of a Precursor and replicated features work together: | ||
{|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | {|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | ||
| − | |-valign="top" -halign="center"| | + | |-valign="top" -halign="center" |
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | [[Image:ReplicationPrecursor.png]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | The next figure shows the unfolded form of classes ''A'' and ''B'' (there is no Precursor call anymore): | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
{|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | {|border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="center" | ||
|-valign="top" -halign="center" | |-valign="top" -halign="center" | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | + | [[Image:ReplicationPrecursorUnfolded.png]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | This will again lead to an invalid system. Features ''a'', ''f'' and ''g'' will be replicated twice each. But feature ''gP'' (the unfolded form for the precursor) won't be replicated. So there will be a call from the shared feature ''gP'' to the not shared feature ''f''. | |
| + | Again, this seems to be against the intuition of the programmer. When there is a replicate for a feature, then there should also be a replicate for its precursor. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Link with other unfolded forms==== | ||
| + | The previous two sections showed that there is a missing link between certain unfolded forms. This article here proposes the concept of a '''name coupling'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The name of the call-equivalent of an inline-agent and the name of its enclosing feature should be coupled together such that when the latter is renamed, the former is renamed too. | ||
| − | + | The same is true for the relative unfolded form of a precursor and the feature itself. | |
| − | + | One question remains, to what name should these features be renamed? The answer is simple, it needs to be a new unique name in the system. | |
Latest revision as of 07:06, 24 January 2007
Author: Matthias Konrad
Related articles:
- A discussion on unfolded forms in the ECMA standard: ECMA_unfolded.
- A mathematical model for Eiffels dynamic binding: DynBindModel.
- An example instantiation of the the dynamic binding model: DynBindModelExamples.
Contents
Prologue
One definition of replication is: the action or process of reproducing or duplicating.
Both ETL, OOSC2 and the standard use the term replication as if its semantics were common knowledge. I disagree to that, since I was not able to get consistent information about replication from notable experts. Hence it is certainly a term to be defined much more carefully.
Although not explicitly stated, it seems that a replicated feature has an unfolded form. That would mean, that we could get rid of replication by reducing it to other language mechanisms (As it is done for precursors). This is how the current ISE compiler (5.7 and earlier) handles replication (won't help us here since it doesn't comply to the standard).
If an unfolded form cannot be found, this has a huge impact on the standards text. The semantics of unqualified calls in the context of replicated features would for example not be defined.
Talking about features
Before digging into the replication rules we need a clear understanding of a feature.
There is a one to one connection between feature and Feature_body. Every feature has exactly one body. Every body belongs to exactly one feature. Meaning that, two different bodies belong to two different features and two different features have two different bodies.
Have a look at this example:
class B feature f do ... end end |
class D inherit B rename f as f1 select f1 end B rename f as f2 redefine f2 end feature f2 do ... end end |
The following sentences apply to the above system:
- The system has two features.
- The feature named f1 in class D and the feature named f in class B are one and the same feature.
- Feature f1 of class D and feature f of class B are the same feature.
- Feature f2 of class D or the feature named f2 in class D. This feature has its body defined in class D.
By saying feature, we indirectly reference a certain Feature_body. Indirectly, because we can say: "feature f of a class D", when the Feature_body of f belongs to an Ancestor class A of D (Given that f is not redeclared on the inheritance path between A and D).
The name of feature f is always the name stated in its Feature_body. A feature may have different names in different classes (through renaming). It is thus legal to say: "Feature f with name fn in class D", when feature f is renamed to fn somewhere along the according inheritance path.
When we talk about feature bodies we are not strictly bound to the bodies occurring in the programs text. We may also denote the bodies that are results of folded forms. Examples are the body of a synonym or the body of a call-equivalent of an inline-agent or the body of a replicate as we will later see.
Version
A version of a feature f is a feature f2 different from f that is a redeclaration from either f or a version of f.
Talking about replicates
The term feature is now clear. A replicated features seems to be just an other feature. But where is its body? In the above Eiffel system there is certainly some replication going on. But there are no bodies for those replicated features.
This informal reasoning suggests that a replicated feature should be defined by an unfolded form. Given that this is defined, there is finally something like a replicated feature. Every replicated feature has a feature from which it is replicated from. It could be said, feature r is a replicate of feature f or feature r is replicated from feature f.
There is an other problem, it needs to be defined, when there is a need for a replicated feature of a certain feature. Altogether there are two things left to be defined.
When is a replicated feature needed
If a class has two feature names that refer to the same feature, both features need to be replicated. If a class has two features f1 and f2 where f2 is a version of f1 then feature f1 needs to be replicated.
For the above Eiffel system with classes B and D there is a need for replication. The feature with name f2 in class D is a version of the feature with name f1 in D.
The replicated feature
The replicated feature r of a feature f is a redeclaration of f. The body of r is almost a copy of feature f. Some features need to be renamed. In principal it is a transposition of feature f to the class in which the replication is needed. How exactly the transposition is done needs some thought. Here some examples should give a general understanding.
In the following system:
class B feature f do g end g do ... end end |
class D inherit B rename f as f1, g as g1 select f1, g1 end B rename f as f2, g as g2 end end |
Both feature f and g of class B need to be replicated twice in class D. The unfolded form of D (here called DU) becomes:
class DU inherit B rename f as f1, g as g1 redefine f1, g1 select f1, g1 end B rename f as f2, g as g2 redefine f2, g2 end feature f1 do g1 end g1 do ... end f2 do g2 end g2 do ... end end |
It is somewhat lame not to give a precise definition of how exactly transposition works. But it is used in other places of the Eiffel standard as well and is thus off topic to describe it here.
Replication and inline agents
It is important to analyze how this new unfolded form works together with other unfolded forms. The following system contains both an inline-agent and some features that need to be replicated:
The unfolded form of the inline agent is a normal feature in class A. The replicated features become a redeclaration of features f and g. The following picture shows the same system with everything unfolded:
According to the current Eiffel standard this system is not valid anymore. Shared feature x is not allowed to refer to the replicated features g1 and g2. Feature x not being replicated comes from the fact, that class B inherits from the completely unfolded class A. Otherwise the unfolding would become ambiguous. The unfolded system is most probably not what the programmer had in mind when he constructed it. He certainly expected feature x of the inline agent to be replicated too. At the moment though, there is no such link between the inline-agent and its enclosing feature (feature f)
Replication and precursor
The problem discussed here is similar to the previous one. It shows how the unfolded form of a Precursor and replicated features work together:
The next figure shows the unfolded form of classes A and B (there is no Precursor call anymore):
This will again lead to an invalid system. Features a, f and g will be replicated twice each. But feature gP (the unfolded form for the precursor) won't be replicated. So there will be a call from the shared feature gP to the not shared feature f. Again, this seems to be against the intuition of the programmer. When there is a replicate for a feature, then there should also be a replicate for its precursor.
Link with other unfolded forms
The previous two sections showed that there is a missing link between certain unfolded forms. This article here proposes the concept of a name coupling.
The name of the call-equivalent of an inline-agent and the name of its enclosing feature should be coupled together such that when the latter is renamed, the former is renamed too.
The same is true for the relative unfolded form of a precursor and the feature itself.
One question remains, to what name should these features be renamed? The answer is simple, it needs to be a new unique name in the system.