Difference between revisions of "Using Dialog Prompts (Advanced)"
m |
m |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Extending_EiffelStudio]] |
| − | + | [[Category:EiffelStudio Foundations]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | There are two methods of displaying dialog prompts inside [[:Category:EiffelStudio|EiffelStudio]]. Firstly there is the simple and effective approach, which requires very little coding but offers very little in the way of customization. The second approach can be simple, but by not means as simple as the first, and can offer a great deal of customization. The information in this page pertains for the latter approach. To use the former please see [[Using Dialog Prompts (Basic)]]. | |
| − | + | == Getting Started == | |
| + | If you have ended up here then you are either curious or have decided that you want to use some of the extended features of the [[:Category:EiffelStudio|EiffelStudio]] [[Tool Dialog Prompts]]. The page is given the title "Advanced" and there are more advanced topics here but using the deep level of customization features is for everyone as it's simple enough to use. | ||
Before continuing you may also want to check out the following pages: | Before continuing you may also want to check out the following pages: | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
* [[Dialog Prompt Messages and Formatting]] | * [[Dialog Prompt Messages and Formatting]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Introducing the Dialog Prompt Classes == |
| − | + | There are, as of [[:Category:EiffelStudio|EiffelStudio]] [[EiffelStudio_6.1_Releases|6.1]], four common dialog prompt classes for use which are somewhat self-explanatory. | |
| − | [[ | + | * [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_error_prompt.e ES_ERROR_PROMPT]: Used to display a error. |
| + | * [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_warning_prompt.e ES_WARNING_PROMPT]: Used to display a warning | ||
| + | * [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_information_prompt.e ES_INFORMATION_PROMPT]: Used to display a piece of informative text. | ||
| + | * [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_question_prompt.e ES_QUESTION_PROMPT]: Used to ask the user a yes/no question. | ||
| + | All dialog prompt classes are based on an abstract implementation [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_prompt.e ES_PROMPT]. | ||
| − | + | {{Note| There is a running convention in [[:Category:EiffelStudio|EiffelStudio]] (for classes prefixed with <eiffel>ES_</eiffel>) whereby all dialog prompts end in <eiffel>_PROMPT</eiffel>. From this you can determine if there are any specialized dialog prompts available for you to use, as the base implementation in [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_prompt.e ES_PROMPT] is customizable. You can also use the code browsing tools to check for all descendents of [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_prompt.e ES_PROMPT].}} | |
| − | + | Each dialog prompt class provide two or more creation routines; <eiffel>make</eiffel> and <eiffel>make_standard</eiffel>. Some prompt classes also have an addition creation routine, <eiffel>make_standard_with_cancel</eiffel>, to augment the standard button set with a '''Cancel''' button. The creation routine <eiffel>make</eiffel> offers the most control but requires more information to create the dialog and some understanding of the concpt of a [[Dialog Buttons Sets]]. The <eiffel>make_standard</eiffel> creation routines are simpler and only require a dialog prompt message, just like the basic dialog prompt usage detailed in [[Using Dialog Prompts (Basic)]]. | |
| − | + | == Dialog Prompt Buttons == | |
| − | + | The <eiffel>make_standard</eiffel> creation routines initialize the dialog prompt using a standard set of dialog buttons in the order dictated by the executing platform. The standard dialog buttons are as follows (ordering representative on Windows): | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * Error: '''Ok''' | |
| + | * Warning: '''Ok''' | ||
| + | * Information: '''Ok''' | ||
| + | * Question: '''Yes'''|'''No''' | ||
| − | + | As mentioned, some of the prompts come with a third creation routine, <eiffel>make_standard_with_cancel</eiffel>, augmenting the existing dialog prompt's button set with a '''Cancel''' button. The only dialog prompt not to have a third creation routine is the Error prompt as an error is usual considered an exception case and general there is no recourse action. The standard dialog buttons "with cancel" are as follows (ordering representative on Windows): | |
| − | + | * Warning: '''Ok'''|'''Cancel''' | |
| + | * Information: '''Ok'''|'''Cancel''' | ||
| + | * Question: '''Yes'''|'''No'''|'''Cancel''' | ||
| − | + | For a more visual demonstration see [[Taxonomy of Dialog Prompts#Choosing a Type|Taxonomy of Dialog Prompts]]. | |
| − | === | + | === Button Sets === |
| + | Most dialog prompts have a standard set of buttons and being so [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/es_dialog_buttons.e ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS] provides access to the well-known and commonly used button sets, such as '''Ok'''|'''Cancel''', '''Yes'''|'''No''' and even '''Abort'''|'''Retry'''|'''Ignore'''. | ||
| − | + | {{Note|All dialog prompts inherit [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/shared/es_shared_dialog_buttons.e ES_SHARED_DIALOG_BUTTONS] through the base dialog implementation [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/es_dialog.e ES_DIALOG] (see [[Tool Dialogs]] for more information on [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/es_dialog.e ES_DIALOG] and dialog button sets.)}} | |
| − | + | For information of button set and creating your own button set see [[Dialog Buttons Sets]]. | |
| − | + | === Setting Default Buttons === | |
| − | === Default | + | ==== Default Active Button ==== |
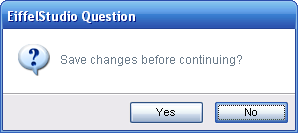
| + | Every prompt has a default active button, also known as the "Default Button". This is the button that will have the focus when the dialog is shown. In the following dialog prompt the '''No''' button is the default button. | ||
| − | + | <eiffel> | |
| + | ask_save_changes | ||
| + | -- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing | ||
| + | local | ||
| + | l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT | ||
| + | do | ||
| + | create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?") | ||
| + | l_prompt.show_on_active_window | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Dialog prompts example question no default.png|No is the default set default button]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''No''' was set as the default-default button automatically. Unless set, every dialog prompt uses the least dangerous button as the default button. In the above example '''No''' is actually set as the automatic default button because '''No''' is considered (statically) the least dangerous button for question prompts. If the question prompt was created with <eiffel>make_standard_with_cancel</eiffel> the '''Cancel''' button would actually be the default button because '''Cancel''' is considered less dangerous than '''No'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To override the default behavior you'll need to specify the default button. This has to be a button identifier for a button that exists on the dialog prompt. The following code demonstrates this. | ||
<eiffel> | <eiffel> | ||
| Line 52: | Line 78: | ||
-- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing | -- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing | ||
local | local | ||
| − | l_prompt: | + | l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT |
do | do | ||
| − | create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing? | + | create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?") |
| − | l_prompt. | + | l_prompt.set_default_button ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button) |
l_prompt.show_on_active_window | l_prompt.show_on_active_window | ||
end | end | ||
</eiffel> | </eiffel> | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Dialog prompts example question default.png|Yes is now the default button]] |
| + | ==== Default Confirm Button ==== | ||
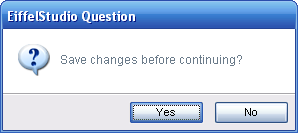
| + | The default confirm button is another default button, but this setting for this button has no visible cue as the [[#Default Active Button|Default Active Button]] does. Instead the default confirm button is the button that is selected when the user opts to confirm a default action on the dialog using {{Key|CTRL+ENTER}}, once the dialog prompt is show. | ||
| − | + | The default confirm button can be set using <eiffel>set_default_confirm_button</eiffel>: | |
| − | + | <eiffel> | |
| − | + | ask_save_changes | |
| − | + | -- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing | |
| + | local | ||
| + | l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT | ||
| + | do | ||
| + | create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?") | ||
| + | l_prompt.set_default_confirm_button ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button) | ||
| + | l_prompt.show_on_active_window | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Dialog prompts example question no default.png|No is the default set default button]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | In the above code the [[#Default Active Button|default active button]] is actually the '''No''' button but the default action button is the '''Yes''' button. Press {{key|CTRL+ENTER}} will selected '''Yes''', whereas pressing {{key|ENTER}} or {{key|SPACE}} will select the focused (active) button '''No'''. | |
| − | + | {{Note| The functionality whereby the user can press CTRL+ENTER, is inherited behavior from top most inherited class [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/es_dialog.e ES_DIALOG].}} | |
| − | {{ | + | ==== Default Cancel Button ==== |
| + | There also exists a default cancel button, which is selected when the user presses {{key|ESC}} or closes the dialog prompt without pressing one of the dialog prompt buttons. Like the [[#Default Active Button|default active button]], this behavior is inherited from [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/es_dialog.e ES_DIALOG]. The cancel buttons should always be associated with the '''Cancel''' button, if it exists, or be associated with the least dangerous button on the prompt. | ||
| − | + | You can set the default cancel button just like you can the [[#Default Active Button|default active button]] and [[#Default Confirm Button|default confirm button]] using <eiffel>set_default_cancel_button</eiffel>: | |
<eiffel> | <eiffel> | ||
| Line 85: | Line 121: | ||
-- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing | -- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing | ||
local | local | ||
| − | l_prompt: | + | l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT |
do | do | ||
| − | create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing? | + | create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?") |
| − | l_prompt. | + | l_prompt.set_default_cancel_button ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.no_button) |
l_prompt.show_on_active_window | l_prompt.show_on_active_window | ||
end | end | ||
</eiffel> | </eiffel> | ||
| − | [[ | + | === Responding to User Interactions === |
| + | [[:Category:EiffelStudio|EiffelStudio]] dialog prompts offer a dual interaction model when responding to user interaction. This frees you from the bounds of choosing one model over the other and lifts the restrictions on using either a single model. Sometimes it may be necessary to use both models. That said, the use of agents if the preferred model inside [[:Category:EiffelStudio|EiffelStudio]]. | ||
| + | ==== Agent Assignment ==== | ||
| + | The primary model is the use of [http://docs.eiffel.com/eiffelstudio/general/guided_tour/language/tutorial-12.html agents], assigning them to a button using a button identifier. | ||
| − | + | After creating a prompt you may associate an agent to a button using <eiffel>[https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_prompt.e ES_PROMPT].set_button_action</eiffel>. The routine takes a button identifier, which must be an identifier of a button on the prompt, as well as an agent action. | |
| − | + | <eiffel> | |
| + | ask_save_changes | ||
| + | -- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing | ||
| + | local | ||
| + | l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT | ||
| + | do | ||
| + | create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?") | ||
| + | l_prompt.set_button_action ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button, agent save_changes) | ||
| + | l_prompt.show_on_active_window | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | |||
| + | save_changes | ||
| + | -- Save all changes | ||
| + | do | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the example a question prompt was created using the standard set of buttons for question prompts, which in this case are '''Yes''' and '''No''' buttons. Post-creation and initialization the '''Yes''' button is assigned an agent through the call to <eiffel>set_button_action</eiffel>. <eiffel>set_button_action</eiffel> is passed the button identifier <eiffel>yes_button</eiffel>, which is statically accessed from [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/es_dialog_buttons.e ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS]. <eiffel>yes_button</eiffel> could have just as easily been accessed from the <eiffel>dialog_buttons</eiffel> function exported on the prompt class: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <eiffel> | ||
| + | l_prompt.set_button_action (l_prompt.dialog_buttons.yes_button, agent save_changes) | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
| + | |||
| + | However, static access if preferred if appropriate for the situation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Using Dialog Results ==== | ||
| + | The second model of processing actions or changing execution flow, based on the user's interaction with the dialog prompt, is through the result <eiffel>dialog_result</eiffel>. Like button identifiers, <eiffel>dialog_result</eiffel> is an <eiffel>INTEGER</eiffel> and is set once the dialog has been closed buy the result of a user's interaction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here is the same example written using the dialog result model. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <eiffel> | ||
| + | ask_save_changes | ||
| + | -- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing | ||
| + | local | ||
| + | l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT | ||
| + | do | ||
| + | create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?") | ||
| + | l_prompt.show_on_active_window | ||
| + | |||
| + | if l_prompt.dialog_result = {ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button then | ||
| + | save_changes | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | |||
| + | save_changes | ||
| + | -- Save all changes | ||
| + | do | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using static access for the dialog button identifiers also allows you to opt to use the Eiffel <eiffel>inspect</eiffel> construct instead of using <eiffel>if</eiffel>...<eiffel>then</eiffel>...<eiffel>elseif</eiffel>...<eiffel>then</eiffel>...<eiffel>end</eiffel>: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <eiffel> | ||
| + | inspect l_prompt.dialog_result | ||
| + | when {ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button then | ||
| + | save_changes | ||
| + | when {ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.no_button then | ||
| + | do_something_else | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Changing Button Labels === | ||
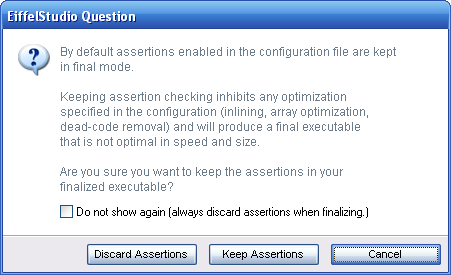
| + | There are times when a dialog prompt's button labels are not adequate enough to get the full message over to the user, or simply that you want a dialog prompt's buttons to show an extremely terse explaination of their action. Once such dialog in [[:Category:EiffelStudio|EiffelStudio]] is the Discard Assertions question prompt: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Dialog prompts example discard assertions.png|Dialog shown when finalizing an Eiffel project]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The discard assertion dialog prompt is a question prompt that has had it's '''Yes''' button label set to '''Discard Assertions''' and '''No''' button label set to '''Keep Assertions'''. There was no need to subclass [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_question_prompt.e ES_QUESTION_PROMPT] (well actually [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_discardable_question_prompt.e ES_DISCARDABLE_QUESTION_PROMPT] but we have not gotten to discardable dialog prompts yet) and redefine <eiffel>dialog_button_label</eiffel>. Instead <eiffel>set_button_text</eiffel> can be used, in a similar manner as <eiffel>set_button_action</eiffel> is. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <eiffel> | ||
| + | ask_save_changes | ||
| + | -- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing | ||
| + | local | ||
| + | l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT | ||
| + | do | ||
| + | create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?") | ||
| + | l_prompt.set_button_text ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button, "Save Changes") | ||
| + | l_prompt.set_button_action ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button, agent save_changes) | ||
| + | l_prompt.set_button_text ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.no_button, "Continue Without Save") | ||
| + | l_prompt.show_on_active_window | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
| + | |||
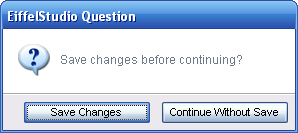
| + | [[Image:Dialog prompts example button text.png|Changing button labels]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Not only has the text been changed on the dialog prompt but the buttons have also been resized and both resized to match each width, as per the general user interface guidelines related to dialog buttons. This is just one of the new features of the new dialog implementation in [[EiffelStudio_6.1_Releases|6.1]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In addition the resizing the key bindings have also been altered. On regular question prompts with '''Yes''' and '''No''' buttons pressing the {{key|Y}} key will select the '''Yes''' button and pressing {{key|N}} will select the '''No''' button. With the buttons relabeled from their defaults new key bindings are introduced. '''Save Changes''' can be select by pressing {{key|S}} and '''Continue Without Save''' selected by pressing {{key|C}}. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Changing the Title, Subtitle and Text == | ||
| + | Most of the dialog prompts in EiffelStudio use a default title, in English it reads "EiffelStudio ''<Type>''" where ''<Type>'' is the type of dialog prompt. The [[:Category:EiffelStudio|EiffelStudio]] [[EiffelDebugger|Debugger]] dialog prompts actually set the title "Debugger ''<Type>''". | ||
| + | |||
| + | Setting the dialog prompt's title is a simple matter of calling <eiffel>set_title</eiffel> with the appropriate text: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <eiffel> | ||
| + | ask_save_changes | ||
| + | -- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing | ||
| + | local | ||
| + | l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT | ||
| + | do | ||
| + | create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?") | ||
| + | l_prompt.set_title ("Save Changes") | ||
| + | l_prompt.show_on_active_window | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
| + | |||
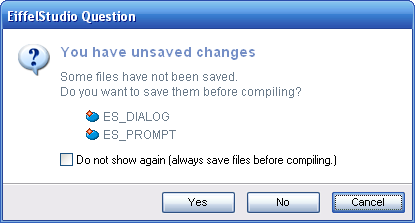
| + | A subtitle is rarely seen in the [[:Category:EiffelStudio|EiffelStudio]] dialog prompts. It is seen in the unsaved changes dialog prompts however. The subtitle in this case is "You have unsaved changes". | ||
[[Image:Dialog prompts example unsaved list.png|Unsaved changes dialog prompt with a subtitle]] | [[Image:Dialog prompts example unsaved list.png|Unsaved changes dialog prompt with a subtitle]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Setting the dialog prompt's subtitle can be done by calling <eiffel>set_subtitle</eiffel> with the appropriate text. Setting the subtitle using an empty string will remove the subtitle from the dialog prompt. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <eiffel> | ||
| + | ask_save_changes | ||
| + | -- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing | ||
| + | local | ||
| + | l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT | ||
| + | do | ||
| + | create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?") | ||
| + | l_prompt.set_title ("Save Changes") | ||
| + | l_prompt.set_subtitle ("You have unsaved changes") | ||
| + | l_prompt.show_on_active_window | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Finally, the actual dialog prompt text can be changed. This is useful if you are reusing a dialog prompt and you need to alter it's text between showings, or if you are using a specialized dialog prompt but you have a need to change the default text. Setting the text can be done by calling <eiffel>set_text</eiffel> on the dialog prompt object. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Avoiding Memory Leaks == | ||
| + | When using agents in dialog prompts it's easy to forget to remove those agents, which can result in memory leaks inside [[:Category:EiffelStudio|EiffelStudio]] as the [[Garbage Collector]] still thinks there is a reference of an object. When using the advanced methods of displaying dialog prompts remember to call <eiffel>recycle</eiffel> once you are finished with your prompt. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <eiffel> | ||
| + | ask_save_changes | ||
| + | -- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing | ||
| + | local | ||
| + | l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT | ||
| + | do | ||
| + | create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?") | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | l_prompt.show_on_active_window | ||
| + | l_prompt.recycle | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </eiffel> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Extending Dialog Prompts == | ||
| + | |||
| + | All dialog prompts are fully extendable. You may either use an existing dialog prompt as your base implementation or you can use [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_prompt.e ES_PROMPT], although using [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_prompt.e ES_PROMPT] requires a little more (simple) implementation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you are implementing a common dialog prompt you can simply examining the existing common dialog implementation for guides. See [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_question_prompt.e ES_QUESTION_PROMPT] for an example on implement a common dialog prompt. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Adding Graphical Elements === | ||
| + | Whether you are using [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_prompt.e ES_PROMPT] or a common dialog prompt as your base implementation, you will need to redefine <eiffel>build_prompt_interface</eiffel> to add graphical widgets to the main dialog prompt's area (the area with a white background.) Be sure to call <eiffel>Precursor</eiffel> to ensure the dialog prompt's [[#Changing the Title, Subtitle and Text| subtitle and text]] are displayed correctly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Adding Buttons and Button Sets === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Changing the buttons, beyond changing their labels is a little more involved. Please see [[Dialog Button Sets]] for information about adding your own buttons sets and button identifiers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you do decided to extend [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/es_dialog_buttons.e ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS] for a specialize dialog prompt, please remember to convariantly redefine <eiffel>dialog_buttons</eiffel> to return an shared instances of your extended version of [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/es_dialog_buttons.e ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS]. This will given dialog prompt clients access to new button identifiers and button sets. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In addition to creating new button identifiers and button sets it is required to redefine <eiffel>dialog_button_label</eiffel> from [https://eiffelsoftware.origo.ethz.ch/svn/es/trunk/Src/Eiffel/interface/new_graphical/dialogs/prompts/es_prompt.e ES_PROMPT]. You implementation should respect the new button identifiers and return a default localized button label. | ||
Latest revision as of 09:19, 14 May 2008
There are two methods of displaying dialog prompts inside EiffelStudio. Firstly there is the simple and effective approach, which requires very little coding but offers very little in the way of customization. The second approach can be simple, but by not means as simple as the first, and can offer a great deal of customization. The information in this page pertains for the latter approach. To use the former please see Using Dialog Prompts (Basic).
Contents
Getting Started
If you have ended up here then you are either curious or have decided that you want to use some of the extended features of the EiffelStudio Tool Dialog Prompts. The page is given the title "Advanced" and there are more advanced topics here but using the deep level of customization features is for everyone as it's simple enough to use.
Before continuing you may also want to check out the following pages:
Introducing the Dialog Prompt Classes
There are, as of EiffelStudio 6.1, four common dialog prompt classes for use which are somewhat self-explanatory.
- ES_ERROR_PROMPT: Used to display a error.
- ES_WARNING_PROMPT: Used to display a warning
- ES_INFORMATION_PROMPT: Used to display a piece of informative text.
- ES_QUESTION_PROMPT: Used to ask the user a yes/no question.
All dialog prompt classes are based on an abstract implementation ES_PROMPT.
![]() Note: There is a running convention in EiffelStudio (for classes prefixed with
Note: There is a running convention in EiffelStudio (for classes prefixed with ES_) whereby all dialog prompts end in _PROMPT. From this you can determine if there are any specialized dialog prompts available for you to use, as the base implementation in ES_PROMPT is customizable. You can also use the code browsing tools to check for all descendents of ES_PROMPT.
Each dialog prompt class provide two or more creation routines; make and make_standard. Some prompt classes also have an addition creation routine, make_standard_with_cancel, to augment the standard button set with a Cancel button. The creation routine make offers the most control but requires more information to create the dialog and some understanding of the concpt of a Dialog Buttons Sets. The make_standard creation routines are simpler and only require a dialog prompt message, just like the basic dialog prompt usage detailed in Using Dialog Prompts (Basic).
Dialog Prompt Buttons
The make_standard creation routines initialize the dialog prompt using a standard set of dialog buttons in the order dictated by the executing platform. The standard dialog buttons are as follows (ordering representative on Windows):
- Error: Ok
- Warning: Ok
- Information: Ok
- Question: Yes|No
As mentioned, some of the prompts come with a third creation routine, make_standard_with_cancel, augmenting the existing dialog prompt's button set with a Cancel button. The only dialog prompt not to have a third creation routine is the Error prompt as an error is usual considered an exception case and general there is no recourse action. The standard dialog buttons "with cancel" are as follows (ordering representative on Windows):
- Warning: Ok|Cancel
- Information: Ok|Cancel
- Question: Yes|No|Cancel
For a more visual demonstration see Taxonomy of Dialog Prompts.
Button Sets
Most dialog prompts have a standard set of buttons and being so ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS provides access to the well-known and commonly used button sets, such as Ok|Cancel, Yes|No and even Abort|Retry|Ignore.
![]() Note: All dialog prompts inherit ES_SHARED_DIALOG_BUTTONS through the base dialog implementation ES_DIALOG (see Tool Dialogs for more information on ES_DIALOG and dialog button sets.)
Note: All dialog prompts inherit ES_SHARED_DIALOG_BUTTONS through the base dialog implementation ES_DIALOG (see Tool Dialogs for more information on ES_DIALOG and dialog button sets.)
For information of button set and creating your own button set see Dialog Buttons Sets.
Setting Default Buttons
Default Active Button
Every prompt has a default active button, also known as the "Default Button". This is the button that will have the focus when the dialog is shown. In the following dialog prompt the No button is the default button.
ask_save_changes
-- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing
local
l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT
do
create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?")
l_prompt.show_on_active_window
end
No was set as the default-default button automatically. Unless set, every dialog prompt uses the least dangerous button as the default button. In the above example No is actually set as the automatic default button because No is considered (statically) the least dangerous button for question prompts. If the question prompt was created with make_standard_with_cancel the Cancel button would actually be the default button because Cancel is considered less dangerous than No.
To override the default behavior you'll need to specify the default button. This has to be a button identifier for a button that exists on the dialog prompt. The following code demonstrates this.
ask_save_changes
-- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing
local
l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT
do
create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?")
l_prompt.set_default_button ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button)
l_prompt.show_on_active_window
end
Default Confirm Button
The default confirm button is another default button, but this setting for this button has no visible cue as the Default Active Button does. Instead the default confirm button is the button that is selected when the user opts to confirm a default action on the dialog using CTRL+ENTER, once the dialog prompt is show.
The default confirm button can be set using set_default_confirm_button:
ask_save_changes
-- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing
local
l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT
do
create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?")
l_prompt.set_default_confirm_button ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button)
l_prompt.show_on_active_window
end
In the above code the default active button is actually the No button but the default action button is the Yes button. Press CTRL+ENTER will selected Yes, whereas pressing ENTER or SPACE will select the focused (active) button No.
![]() Note: The functionality whereby the user can press CTRL+ENTER, is inherited behavior from top most inherited class ES_DIALOG.
Note: The functionality whereby the user can press CTRL+ENTER, is inherited behavior from top most inherited class ES_DIALOG.
Default Cancel Button
There also exists a default cancel button, which is selected when the user presses ESC or closes the dialog prompt without pressing one of the dialog prompt buttons. Like the default active button, this behavior is inherited from ES_DIALOG. The cancel buttons should always be associated with the Cancel button, if it exists, or be associated with the least dangerous button on the prompt.
You can set the default cancel button just like you can the default active button and default confirm button using set_default_cancel_button:
ask_save_changes
-- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing
local
l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT
do
create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?")
l_prompt.set_default_cancel_button ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.no_button)
l_prompt.show_on_active_window
end
Responding to User Interactions
EiffelStudio dialog prompts offer a dual interaction model when responding to user interaction. This frees you from the bounds of choosing one model over the other and lifts the restrictions on using either a single model. Sometimes it may be necessary to use both models. That said, the use of agents if the preferred model inside EiffelStudio.
Agent Assignment
The primary model is the use of agents, assigning them to a button using a button identifier.
After creating a prompt you may associate an agent to a button using .set_button_action. The routine takes a button identifier, which must be an identifier of a button on the prompt, as well as an agent action.
ask_save_changes
-- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing
local
l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT
do
create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?")
l_prompt.set_button_action ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button, agent save_changes)
l_prompt.show_on_active_window
end
save_changes
-- Save all changes
do
...
end
In the example a question prompt was created using the standard set of buttons for question prompts, which in this case are Yes and No buttons. Post-creation and initialization the Yes button is assigned an agent through the call to set_button_action. set_button_action is passed the button identifier yes_button, which is statically accessed from ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS. yes_button could have just as easily been accessed from the dialog_buttons function exported on the prompt class:
l_prompt.set_button_action (l_prompt.dialog_buttons.yes_button, agent save_changes)
However, static access if preferred if appropriate for the situation.
Using Dialog Results
The second model of processing actions or changing execution flow, based on the user's interaction with the dialog prompt, is through the result dialog_result. Like button identifiers, dialog_result is an INTEGER and is set once the dialog has been closed buy the result of a user's interaction.
Here is the same example written using the dialog result model.
ask_save_changes
-- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing
local
l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT
do
create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?")
l_prompt.show_on_active_window
if l_prompt.dialog_result = {ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button then
save_changes
end
end
save_changes
-- Save all changes
do
...
end
Using static access for the dialog button identifiers also allows you to opt to use the Eiffel inspect construct instead of using if...then...elseif...then...end:
inspect l_prompt.dialog_result when {ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button then save_changes when {ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.no_button then do_something_else end
Changing Button Labels
There are times when a dialog prompt's button labels are not adequate enough to get the full message over to the user, or simply that you want a dialog prompt's buttons to show an extremely terse explaination of their action. Once such dialog in EiffelStudio is the Discard Assertions question prompt:
The discard assertion dialog prompt is a question prompt that has had it's Yes button label set to Discard Assertions and No button label set to Keep Assertions. There was no need to subclass ES_QUESTION_PROMPT (well actually ES_DISCARDABLE_QUESTION_PROMPT but we have not gotten to discardable dialog prompts yet) and redefine dialog_button_label. Instead set_button_text can be used, in a similar manner as set_button_action is.
ask_save_changes
-- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing
local
l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT
do
create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?")
l_prompt.set_button_text ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button, "Save Changes")
l_prompt.set_button_action ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.yes_button, agent save_changes)
l_prompt.set_button_text ({ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS}.no_button, "Continue Without Save")
l_prompt.show_on_active_window
end
Not only has the text been changed on the dialog prompt but the buttons have also been resized and both resized to match each width, as per the general user interface guidelines related to dialog buttons. This is just one of the new features of the new dialog implementation in 6.1.
In addition the resizing the key bindings have also been altered. On regular question prompts with Yes and No buttons pressing the Y key will select the Yes button and pressing N will select the No button. With the buttons relabeled from their defaults new key bindings are introduced. Save Changes can be select by pressing S and Continue Without Save selected by pressing C.
Changing the Title, Subtitle and Text
Most of the dialog prompts in EiffelStudio use a default title, in English it reads "EiffelStudio <Type>" where <Type> is the type of dialog prompt. The EiffelStudio Debugger dialog prompts actually set the title "Debugger <Type>".
Setting the dialog prompt's title is a simple matter of calling set_title with the appropriate text:
ask_save_changes
-- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing
local
l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT
do
create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?")
l_prompt.set_title ("Save Changes")
l_prompt.show_on_active_window
end
A subtitle is rarely seen in the EiffelStudio dialog prompts. It is seen in the unsaved changes dialog prompts however. The subtitle in this case is "You have unsaved changes".
Setting the dialog prompt's subtitle can be done by calling set_subtitle with the appropriate text. Setting the subtitle using an empty string will remove the subtitle from the dialog prompt.
ask_save_changes
-- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing
local
l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT
do
create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?")
l_prompt.set_title ("Save Changes")
l_prompt.set_subtitle ("You have unsaved changes")
l_prompt.show_on_active_window
end
Finally, the actual dialog prompt text can be changed. This is useful if you are reusing a dialog prompt and you need to alter it's text between showings, or if you are using a specialized dialog prompt but you have a need to change the default text. Setting the text can be done by calling set_text on the dialog prompt object.
Avoiding Memory Leaks
When using agents in dialog prompts it's easy to forget to remove those agents, which can result in memory leaks inside EiffelStudio as the Garbage Collector still thinks there is a reference of an object. When using the advanced methods of displaying dialog prompts remember to call recycle once you are finished with your prompt.
ask_save_changes
-- Ask user if they want to save the changes before continuing
local
l_prompt: ES_QUESTION_PROMPT
do
create l_prompt.make_standard ("Save changes before continuing?")
...
l_prompt.show_on_active_window
l_prompt.recycle
end
Extending Dialog Prompts
All dialog prompts are fully extendable. You may either use an existing dialog prompt as your base implementation or you can use ES_PROMPT, although using ES_PROMPT requires a little more (simple) implementation.
If you are implementing a common dialog prompt you can simply examining the existing common dialog implementation for guides. See ES_QUESTION_PROMPT for an example on implement a common dialog prompt.
Adding Graphical Elements
Whether you are using ES_PROMPT or a common dialog prompt as your base implementation, you will need to redefine build_prompt_interface to add graphical widgets to the main dialog prompt's area (the area with a white background.) Be sure to call Precursor to ensure the dialog prompt's subtitle and text are displayed correctly.
Adding Buttons and Button Sets
Changing the buttons, beyond changing their labels is a little more involved. Please see Dialog Button Sets for information about adding your own buttons sets and button identifiers.
If you do decided to extend ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS for a specialize dialog prompt, please remember to convariantly redefine dialog_buttons to return an shared instances of your extended version of ES_DIALOG_BUTTONS. This will given dialog prompt clients access to new button identifiers and button sets.
In addition to creating new button identifiers and button sets it is required to redefine dialog_button_label from ES_PROMPT. You implementation should respect the new button identifiers and return a default localized button label.