Difference between revisions of "Transposition"
m |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
With the ECMA Eiffel Standard, the dynamic binding semantics of the Eiffel language are clearly defined. This was not the case before, compiler designers implemented it in a very pragmatic way, that made sense in almost all practical cases. | With the ECMA Eiffel Standard, the dynamic binding semantics of the Eiffel language are clearly defined. This was not the case before, compiler designers implemented it in a very pragmatic way, that made sense in almost all practical cases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:SC_ABC.jpg|450px]] | ||
==Transposition== | ==Transposition== | ||
Revision as of 12:49, 24 October 2006
With the ECMA Eiffel Standard, the dynamic binding semantics of the Eiffel language are clearly defined. This was not the case before, compiler designers implemented it in a very pragmatic way, that made sense in almost all practical cases.
Transposition
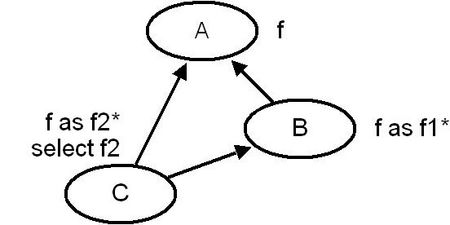
We speak of the transposition of a feature, when we copy an inherited feature to a descendant class and adapt its content according to the inheritance path. When all the inherited features of a class are transposed, we get the flat short form of the class. Transposition is very interesting, since it seems to be the solution to some ambiguities in the language, namely repeated inheritance and replication. In the following system:
class B feature f do g end g do end end |
class D inherit B rename f as f1, g as g1 redefine f1 select f1, g1 end rename f as f2, g as g2 end feature f1 do ... end end |
class D has the transposed form (we omit the features from ANY):
So the transposed form of class D redefines all the features of its parent. Some rather complex rules of the standard become obsolete, when it is just stated, that every inherited feature needs to be transposed (8.16.2, 8.16.3, 8.16.4, 8.16.5). During the transposition there might be conflicts. It is possible that two transposed features have the same name. It remains to be specified how such cases are handled. One solution is to say, that they are valid iif their (transposed) body is equivalent.
Optimization possibilities for transposition
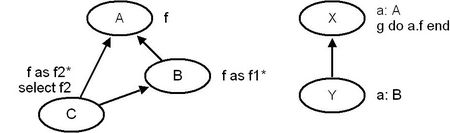
Apart from its power to describe the semantics of the language, transposition is very (mabe too) expensive. It is certainly not acceptable to really transpose every feature from a compiler designer point of view. So we need to find criteria to only transpose when really needed. The following system shows that this is not that easy:
What happens, when an object of class Y with its field a set to an object of class C has its feature g executed. Only the transposition of g to Y gives the answer:
g
do
a.f1
end
The covariant redefinition of a in Y resolved the potential repeated inheritance conflict. Nevertheless, if g wasn't transposed, feature f2 of class C would have been executed. So the transposition was reallly needed here. We may state:
- Every feature that uses a target of a covariant type needs to be transposed (Unqualified feature calls don't have a target).
This rule is actualy to restrictive. If our system wouldn't have contained the class C there wouldn't have been any need to transpose f. But such checks would be very expensive.
- If a feature is not transposition equal ....
Feature g of class X assumes We try to find out, wether it is necessary to really transpose feature g of class Y. The following code snippet gives the answer:
local y: Y c: C do create y create c
Transposition was never necessary in Eiffel compilers but it is now
For the following discussion we use this system of five classes: